Suitable Steel Nails for Efficient and Robust Fastening Solutions
Choosing the right nail for your project can result in a big difference in grip force and appearance.
Factors to Consider
-
Nail size and length
In actual operation, a proper nail length should be 3 times the thickness of the substrate you are nailing through. E.g., A 8-penny nail is suitable to fasten a 1-inch-thick material and a 16-penny nail is suitable to fasten a 2-inch-thick material.
-
Material & coating
Sometimes, the elements of the project will be exposed to outdoor or wet conditions for a long time. If so, except for a proper nail length, an anti-corrosion surface coating is another factor to consider in making the project strong and reliable.
- Electro-galvanized. it is a zinc electrolytic process that adding a thin coating to the carbon steel nails. Electrogalvanizing coating can withstand dry and low-corrosion applications for a few more months or possibly an extra year. But it is not recommended for corrosive environments.
- Hot dipped galvanized. It is an effective way of metal corrosion, mainly used for metal structure on the facilities of the industry. Hot dipped galvanized nails are recommended for pressure treated wood and cedar which can cause standard nails to corrode quickly.
- Stainless Steel 304/316. These types of materials are the appropriate choices for high level corrosion protection requirement. Especially for most exterior applications. 316 grade stainless steel, chromium-nickel alloys, can stand up Marine and corrosive industrial atmospheres.
-
Nail Shank Patterns
The different shank patterns of the nails determine their different uses. The differ basically show in holding power, nailing method and installation effect. The following picture is the main shank patterns we can provide for customer. Special orders can be tailored on your needs.
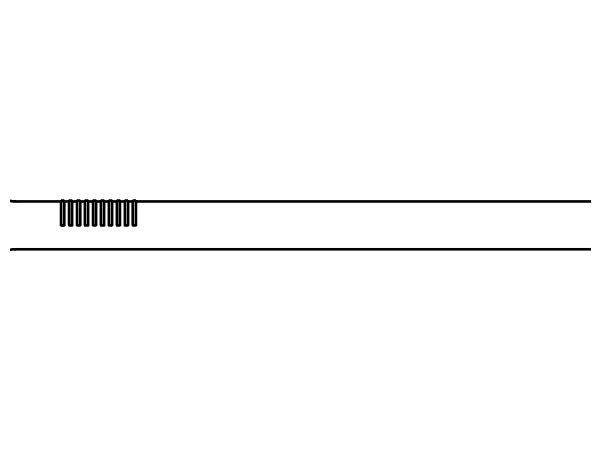
Smooth shank

Ring shank

Screw shank
Square shank

Flute shank

Square twisted shank
-
Other Consideration
For an accurate quotation, the following information are required:
- Nail type.
- Head type and surface.
- Shank type.
- Point type.
- Length.
- Head diameter, shank diameter.
- Surface coating.
- Standards to follow.
- Other characteristic dimensions.